Zero-Knowledge Proof in Blockchain: A Complete Guide to Privacy & Security
Zero-knowledge proof (ZKP) is a cryptographic method where one party (Prover) can prove a statement's truth to another party (Verifier) without revealing any additional information. This encryption scheme, developed by MIT researchers in the 1980s, ensures data privacy while maintaining transaction validity.
Core Properties of Zero-Knowledge Proofs:
- Completeness: Verifier is convinced when statement is true and rules are followed
- Soundness: False statements cannot convince the verifier
- Zero-Knowledge: No information beyond true/false is revealed
Types of Zero-Knowledge Proofs:
- Interactive ZKP: Requires series of actions between prover and verifier
- Non-Interactive ZKP (NIZKP): No interaction needed; challenges generated at once
Key Implementation Areas:
- Secure Messaging
- Authentication Systems
- Storage Protection
- Private Blockchain Transactions
- Complex Documentation
- File System Control
- Vote Verification
- Sensitive Information Protection
Real-World Applications:
- ZCash: Cryptocurrency using zk-SNARKs for shielded transactions
- ING: Modified ZKP system for reduced computational power
- ZCoin: Uses Zerocoin protocol for enhanced security and scalability
Challenges:
- Lack of standardization
- Scalability issues due to high computational requirements
- Complex implementation process
Benefits:
- Enhanced privacy and security
- Simple encryption method
- Shortened blockchain transactions
- Secure data verification without information disclosure
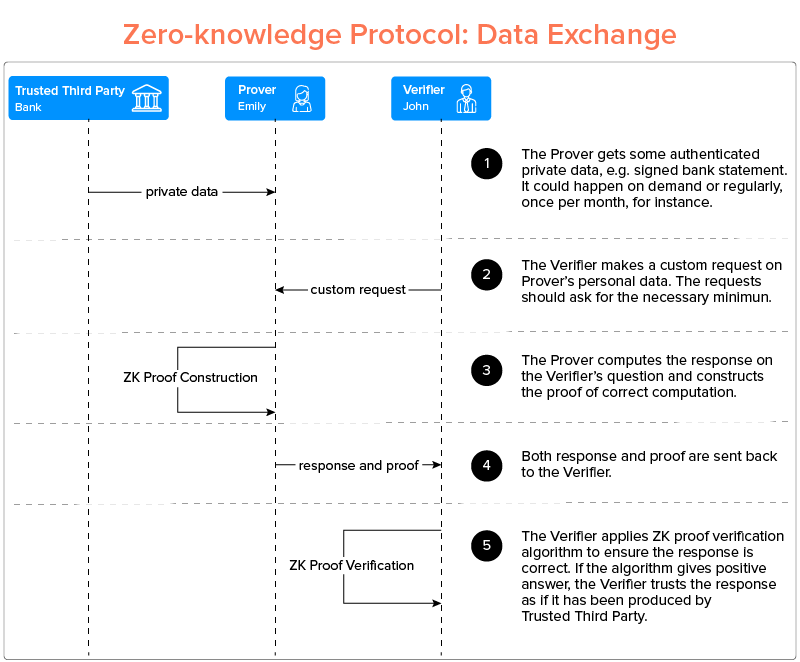
Zero-knowledge proof verification flow diagram
This technology is particularly valuable in blockchain applications where privacy and security are paramount while maintaining transaction transparency and verification capabilities.
Related Articles
Web 3.0 vs Web 2.0: Understanding the Business Impact and Key Differences

